How To Turn A Dedicated Server Into A Cloud?
Let's start with the fact that most people do not make a huge difference between “Cloud Server” and “Dedicated Server”. As long as the technology infrastructure they need works for them at a reasonable monthly cost, they are good. However, the more business owners or authorized employees know about the technology services used by their company, the more informed and the better decisions they will make when it comes to organizing their workflow into the Cloud.
We want to stress that from a technical point of view “cloud” does not mean a “data center”. It also does not mean “Internet”. The term “cloud” refers to an infrastructure environment in which the computation process and the data storage are physically separated workflows.
When an organization uses bare-metal dedicated servers without virtualization technology, the computation and the data storage are separated on two or more different physical servers. In computing, infrastructure setups that consist of 2 or more bare-metal dedicated servers are called clusters.
If an organization uses:
1. Dedicated Hosting - bare-metal servers virtualized with any virtualization technology (Kernel-based Virtual Machine, VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, Xen, Linux Containers, Kubernetes) or;
2. Virtualized servers (Cloud Servers) that reside on top of any cluster of physical servers and if;
3. the process of computation and the data storage are organized in separate virtual or physical servers, part of different physical appliances...
then there is a Cloud, a Cloud infrastructure in place
Cloud is not just about scaling up and down the computing capacity, and it is certainly not about billing, it is not about charing the clients per hour.
So, your organization can have a “Cloud” or virtual or a Cloud of physical servers. To have your own secure enterprise-grade cloud infrastructure, your company does not need to use Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, or any other major cloud service, provider. In fact the smaller the cloud is the better for your organization. Why? Because the smaller infrastructures will charge you less and will provide you with much better technical support, the latter will often come at no additional cost.
If you have privacy concerns related to Cloud services, we suggest you read the article A Data Privacy Issue On The Cloud? Consider It Resolved!. Now we will tell you how to build your Cloud infrastructure using one or more dedicated servers.
Depending on your requirements and the monthly budget you can use:
- One bare-metal dedicated server with internal storage
- Cloud infrastructure (few or more bare-metal servers) with storage area network (SAN)
- Hyper-converged Cloud infrastructure
One Bare-metal Dedicated Server to Cloud
Using one physical server to create a Cloud infrastructure means that your organization will use different Cloud Servers (Virtual Servers), hosted on the same underlying physical appliance. There will be little or no hardware redundancy on such a setup, however. Strictly speaking, if you choose to use one physical dedicated server, your organization will use “Virtual Private Servers”, not “Cloud Servers”. On such a stand-alone physical server, the computation (CPU, RAM) process and the data storage can be organized in separate virtual servers (virtual machines). However, all the applications hosted on a such setup will work on the same physical appliance.
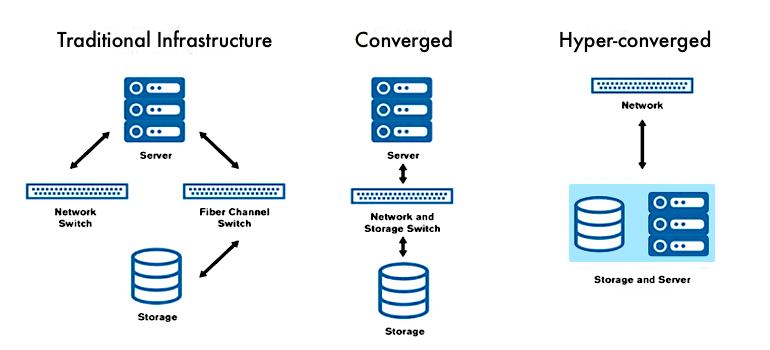
Cloud Infrastructure with SAN
This is a model of Cloud infrastructure where few or more bare-metal servers Or virtual servers provide CPU and RAM resources while the data reside on a separate storage area network (SAN). This is a Cloud system in which two or more physical servers are connected directly one to another or through a network switch. The computation tasks and the data storage operations are divided into different physical sub-systems and different appliances. In Cloud architectural model there are two computing groups:
- Group A – a cluster of processing nodes - physically separate interconnected servers - that deal with operations CPU & RAM
- Group B – storage area network (SAN) – one or more data storage servers, physically separate from the cluster of processing nodes
Both infrastructure groups – Group A and Group B – are interconnected with low latency interconnection network interfaces – 10-gigabit, 20-gigabit, 40-gigabit, etc.
The infrastructures that use storage area networks (SAN) can be designed as 100% uptime guarantee Cloud systems if the data storage appliances feature redundant, therefore are uninterruptible. There are different methods to ensure the operational continuity of storage area networks.
Hyper-Converged Cloud Infrastructure
Hyper-converged infrastructure is a Cloud architectural model in which a number of virtualized physical dedicated servers work as a group to deliver computation and data storage services. All servers part of a hyper-converged cloud work as part of a distributed infrastructure platform. There is software automation, a distributed software layer that makes it possible for all processing resources (CPU and RAM), and the storage drives in the physical dedicated servers to work together. The software layer that runs on each server node, part of the hyper-converged cloud infrastructure, distributes all operating functions across the whole cluster of server nodes.
Hyper-converged infrastructures feature superior performance and resilience. They guarantee 100% uptime, even if 30% of the underlying physical infrastructure is not available.
The first step to turn a dedicated server into cloud infrastructure is to virtualize it with any enterprise virtualization technology. Proxmox Virtualization for example allows organizations to use two different types of virtualization technologies – Kernel-based Virtual Machine and Linux Containers to create a cloud infrastructure of one or more servers. Proxmox Virtualization and other enterprise virtualization technologies can be used to create a “Dedicated Cloud with one bare-metal dedicated server with internal storage” or a “ Cloud infrastructure of few or more bare-metal servers with storage area network (SAN)”. VMware and some other enterprise virtualization technologies allow organizations to build hyper-converged cloud infrastructures.
The most economical and efficient way to create your own, dedicated cloud infrastructure is to start with one or two servers and to use Proxmox VE or any other enterprise virtualization. For that, find a consultant or use any Managed Cloud service provider like ServerWhere.com. Our dedicated servers are resource-rich and powerful enough to be used for building a cost-effective and resilient Cloud infrastructure.